 自然保护与休闲部
自然保护与休闲部保护·守护·共享
 自然保护与休闲部
自然保护与休闲部 目录
目录沿海平原/山麓低地森林
这是一片多样化的森林群,由暂时被洪水淹没到季节性被洪水淹没的森林组成,占据着沿海平原和外山麓的洪泛区和河流阶地。它包括所有排水相对良好的堤坝森林和较高台地,以及不以落羽杉 ( Taxodium distichum ) 和沼泽树 ( Nyssa spp.) 为主的湿润沼泽。在较大的沿海平原河床中,微地形异质性非常高,如果不反复观察和研究,就很难确定洪水频率和持续时间。这个大群体中的群落倾向于沿着相交的梯度进行分类,这些梯度包括河流水位以上的相对海拔、水文周期、土壤排水、土壤质地和土壤肥力。
Characteristic tree species vary with stream order, soil type, flooding regime, and successional status. High, infrequently flooded terraces along brownwater rivers (e.g., the Nottoway) of southeastern Virginia support swamp chestnut oak (Quercus michauxii), cherrybark oak (Quercus pagoda), shagbark hickory (Carya ovata), and sweetgum Liquidambar styraciflua), with an understory of deciduous holly (Ilex decidua), American hornbeam (Carpinus caroliniana ssp. caroliniana and ssp. virginiana), Elliott's blueberry (Vaccinium elliottii), parsley hawthorn (Crataegus marshallii), and other species of relatively well-drained soils. In the same drainages, low terraces or swales on higher terraces support forests of green ash (Fraxinus pennsylvanica), water hickory (Carya aquatica), overcup oak (Quercus lyrata), and laurel oak (Quercus laurifolia), often with a minor component of bald cypress (Taxodium distichum) and water tupelo (Nyssa aquatica). These forests are usually flooded during the winter and early spring but exposed during much of the growing season. Their understory is typically open, with sedges and grasses (especially Carex typhina, Carex louisianica, and Leersia lenticularis) dominant in the herb layer. Analogous communities of the Piedmont and northern Coastal Plain are similar but with overstory dominance by willow oak (Quercus phellos) and pin oak (Quercus palustris).

北部沿海平原最潮湿的沼泽通常以绿梣和红枫( Acer rubrum )为主,草本层中则有大量水生草本植物,如蜥蜴尾( Saururus cernuus )。沼泽森林的草本层含有许多能够很好地适应水位波动的物种,并且通常具有与洪水和水位下降周期相关的明显季节性特征。在早期,淹没较深的微生境可能完全被挺水植物所主导,例如东部甘草( Glyceria septentrionalis ) 、沼泽酸模 ( Rumex verticillatus ) 和弗吉尼亚蓝菖蒲 ( Iris virginica )。季末的消落区通常长满了茂盛的普通木芦苇 ( Cinna arundinacea ) 和草本植物,例如蜥蜴尾、假荨麻 ( Boehmeria cylindrica )、小鬼针草 ( Bidens discoidea )、翅猴花 ( Mimulus alatus )、疯狗草 ( Scutellaria lateriflora ) 和密花蓼 ( Persicaria densiflora )。由于其景观连续性、水源充足以及多方面的食物和栖息地资源,这些沼泽对于多样化动物种群的保护尤为重要。这些群落通常为各种筑巢鸟类、哺乳动物、无脊椎动物、爬行动物和两栖动物提供支持。
在内陆海岸平原和南部皮埃蒙特河流的沙质堤坝和排水良好的阶地上,林分通常缺乏显著的橡树成分,而是包含梧桐 ( Platanus occidentalis )、枫香树 ( Liquidambar styraciflua )、朴树 ( Celtis occidentalis和Celtis laevigata )、美国榆树 ( Ulmus americana )、河桦树 ( Betula nigra )和绿梣树的混合冠层。在弗吉尼亚州中东部的帕蒙基河、马塔波尼河和拉帕汉诺克河的洪泛区,记录到有一片茂密的洪泛区森林,其中生长着美洲山毛榉( Fagus grandifolia )、山核桃( Carya cordiformis )、舒马德橡树( Quercus shumardii )、沼泽栗橡树和多种需要营养的草本植物。在小河底部,冲积地貌和栖息地条件的规模非常小,堤坝和沼泽的典型树木可能以混合林的形式出现。在排水良好的小河底部,鹅掌楸( Liriodendron tulipifera )通常很重要。林下植物和草本植物的组成随地理和立地条件的不同而变化很大。
参考文献:Crouch( 1990 )、Fleming( 2002 a)、Fleming 和 Moorhead( 1998 )、Frost 和 Musselman( 1987 )、Glascock 和 Ware( 1979 )、McCoy 和 Fleming( 2000 )、Parker 和 Wyatt( 1975 )、Parsons 和 Ware( 1982 )、Rheinhardt 等人。( 2000 ),Walton 等人( 2001 )。
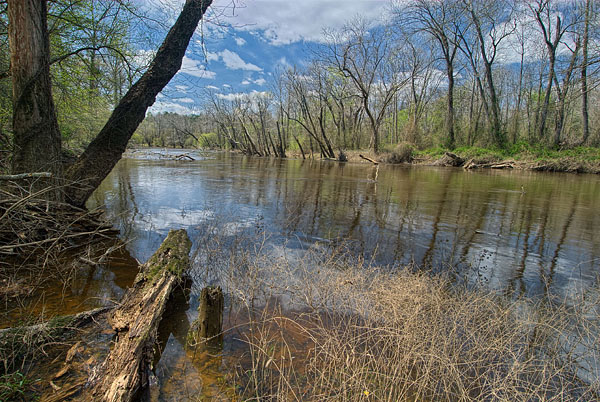 © DCR-DNH,加里·P·弗莱明。
© DCR-DNH,加里·P·弗莱明。
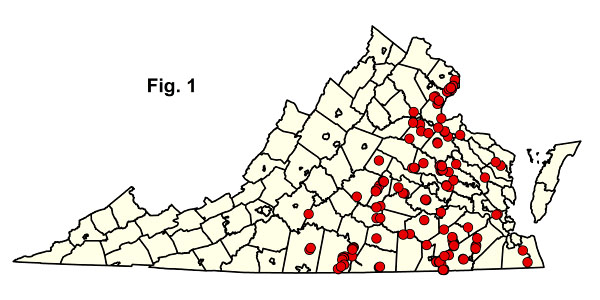
 下载下面列出的每个社区类型的组成汇总统计电子表格。
下载下面列出的每个社区类型的组成汇总统计电子表格。