 自然保护与休闲部
自然保护与休闲部保护·守护·共享
 自然保护与休闲部
自然保护与休闲部 目录
目录山地/山麓渗流沼泽
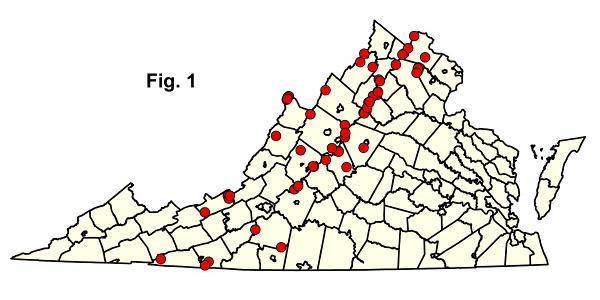
这片饱和的森林湿地位于缓坡溪流源头、大型泉眼以及山沟和溪底的侧边区域,地下水从山坡底部涌出。这些社区分散分布于西弗吉尼亚州各地,从最低海拔到远高于1200米( 4 , 000英尺)。栖息地通常具有丘陵和洼地微地形,覆盖着大量的巨石、鹅卵石和砾石冲积层;辫状渗水和河道;苔藓覆盖的丘陵;以及充满淤泥的洼地。从水文角度来看,这些栖息地被归类为“地下水坡地湿地”,其中从地表排出的渗漏水会以溪流的形式排走。它们不同于某些盆地湿地,这些盆地湿地严格由悬浮地下水饱和并支持类似的植被(有关更多信息,请参阅山地洼地沼泽和池塘生态群描述)。六种群落类型根据土壤和地下水化学、海拔和地理梯度而分离。
The Central Appalachian Basic Seepage Swamp occurs at elevations up to 975 m (3,200 ft) in areas underlain by metabasalt (greenstone) and other mafic rocks, base-rich granitic rocks, calcareous shale, and limestone. The type is most common on the northern Blue Ridge but is found occasionally in the Ridge and Valley province, and rarely in the western Piedmont. Soils range from strongly acidic to circumneutral, with moderately high calcium and magnesium levels. Overstory composition is mixed, with variable combinations of red maple (Acer rubrum), white ash (Fraxinus americana), black ash (Fraxinus nigra), tulip-tree (Liriodendron tulipifera), and sweet birch (Betula lenta var. lenta). Yellow birch (Betula alleghaniensis) is an important tree at some sites. Spicebush (Lindera benzoin var. benzoin) is usually the most abundant shrub. Herbaceous cover is typically lush, and often features patch-dominance of skunk cabbage (Symplocarpus foetidus), American false-hellebore (Veratrum viride), and/or sedges (especially Carex bromoides ssp. bromoides and Carex prasina). Additional characteristic herbs include marsh marigold (Caltha palustris var. palustris), golden saxifrage (Chrysosplenium americanum), swamp saxifrage (Micranthes pensylvanica), lettuce saxifrage (Micranthes micranthidifolia), marsh blue violet (Viola cucullata), golden ragwort (Packera aurea), orange jewelweed (Impatiens capensis), water-hemlock (Cicuta maculata var. maculata), large purple fringed orchid (Platanthera grandiflora), and various ferns. Most Virginia populations of the globally rare plants bog bluegrass (Poa paludigena) and glade spurge (Euphorbia purpurea), as well as of the globally rare Blue Ridge Mountain amphipod (Stygobromus spinosus), are associated with these basic-soil swamps.
Acidic analogues of the preceding type occur in the same region on soils weathered from sandstone, quartzite, or base-poor granitic rocks. Abundant Sphagnum mats and groundwater with low pH are typical habitat features. Soils are very strongly to extremely acidic, with low base status. Composition is variable over the range of this group. Red maple (Acer rubrum), blackgum (Nyssa sylvatica), and tulip-poplar (Liriodendron tulipifera), are the most typical trees, while winterberry (Ilex verticillata), swamp azalea (Rhododendron viscosum var. viscosum), highbush blueberries (Vaccinium corymbosum and Vaccinium fuscatum) are abundant shrubs. Pitch pine (Pinus rigida) is a characteristic tree of some Ridge and Valley stands. Skunk-cabbage (Symplocarpus foetidus) and American false-hellebore (Veratrum viride) may be as dominant in these communities as in Mountain / Piedmont Basic Seepage Swamps; herbs and low shrubs more abundant in or characteristic of acidic swamps include cinnamon fern (Osmundastrum cinnamomeum), bristly dewberry (Rubus hispidus), kidneyleaf grass-of-parnassus (Parnassia asarifolia), yellow fringed orchid (Platanthera ciliaris) small green wood orchid (Platanthera clavellata), common tree clubmoss (Lycopodium obscurum), white-edged sedge (Carex debilis), and long sedge (Carex folliculata). Like the very similar Coastal Plain / Piedmont Acidic Seepage Swamps, these communities support populations of the federally listed swamp-pink (Helonias bullata).

Seepage swamps above 975 m (3,200 ft) elevation are compositionally allied with more northern vegetation types. Eastern hemlock (Tsuga canadensis), yellow birch (Betula alleghaniensis), and red maple (Acer rubrum) are the most common trees. Locally, red spruce (Picea rubens) or eastern white pine (Pinus strobus) may be co-dominants. Shrub layer composition and density is variable; deciduous hollies (Ilex verticillata and Ilex montana), several blueberries (particularly Vaccinium corymbosum, Vaccinium simulatum, and Vaccinium angustifolium), great rhododendron (Rhododendron maximum), mountain laurel (Kalmia latifolia), speckled alder (Alnus rugosa), and witch hazel (Hamamelis virginiana var. virginiana) may be abundant. Characteristic herbs of these swamps include marsh marigold (Caltha palustris var. palustris), star sedge (Carex echinata ssp. echinata), finely-nerved sedge (Carex leptonervia), eastern rough sedge (Carex scabrata), three-seeded sedge (Carex trisperma), slender wood reedgrass (Cinna latifolia), tall flat-topped white aster (Doellingeria umbellata var. umbellata), spinulose wood fern (Dryopteris carthusiana), slender mannagrass (Glyceria melicaria), whorled wood aster (Oclemena acuminata), cinnamon fern (Osmundastrum cinnamomeum), American false-hellebore (Veratrum viride), and smooth white violet (Viola mackloskeyi var. pallens). Communities in this group are naturally rare due to the scarcity of flat or gentle, wet habitats in the higher Appalachians.
所有渗流沼泽都是易受水文干扰的小斑块群落。海狸已经在多个地点部分破坏了这些沼泽的优良典范,由于铁杉绵蚜( Adelges tsugae )的爆发,大量铁杉死亡,损害了许多林分的完整性。目前,阿巴拉契亚山脉中部基本渗流沼泽的大量灰烬成分因翡翠灰螟的爆发而遭受严重死亡。
参考文献:Allard 和 Leonard ( 1943 )、Carr ( 1939 )、Fleming ( 1999 )、Fleming ( 2002 b)、Fleming 和 Van Alstine ( 1990 、Fleming 和 Coulling ( 2001 )、Rawinski 等人 ( 1994 )、Rawinski 等人 ( 1996 )。 © DCR-DNH,加里·P·弗莱明。
© DCR-DNH,加里·P·弗莱明。
 下载下面列出的每个社区类型的组成汇总统计电子表格。
下载下面列出的每个社区类型的组成汇总统计电子表格。