 自然保护与休闲部
自然保护与休闲部保护·守护·共享
 自然保护与休闲部
自然保护与休闲部 目录
目录泥炭地大西洋白雪松森林
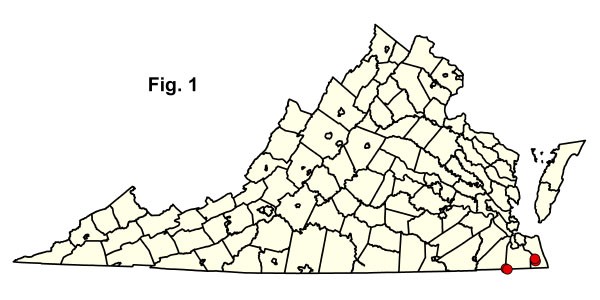
In Virginia, these coniferous forests are confined to saturated, oligotrophic, Coastal Plain peatlands. Peatland Atlantic White-Cedar Forests are endemic to terraces of the Embayed Region of extreme southeastern Virginia and northeastern North Carolina. Habitats are non-riverine wetland flats with deep organic soils (e.g., Great Dismal Swamp, Cities of Suffolk and Chesapeake) and remote peat flats beyond the range of wind-tidal flooding along the North Landing River (City of Virginia Beach). Atlantic white-cedar forests usually occupy relatively wet peatlands subject to infrequent catastrophic fires. Dense, even-aged stands become established when such fires remove most vegetation and debris, exposing suitable seedbeds. Throughout their maturation, these stands accumulate extensive dead wood and inflammable duff, making them increasingly susceptible to another stand-killing fire. Atlantic white-cedar (Chamaecyparis thyoides) dominates the overstory, sometimes with red maple (Acer rubrum), swamp tupelo (Nyssa biflora), or pines (Pinus serotina and Pinus taeda) as minor associates. Red bay (Persea palustris), sweetbay magnolia (Magnolia virginiana var. virginiana), sweet pepperbush (Clethra alnifolia), big gallberry (Ilex coriacea), inkberry (Ilex glabra), shining fetterbush (Lyonia lucida), and poison ivy (Toxicodendron radicans var. radicans) are common small trees and shrubs. Cinnamon fern (Osmundastrum cinnamomeum) and Virginia chain fern (Woodwardia virginica) are common herbs, while (Sphagnum spp.) and other mosses abundantly cover the ground.

泥炭地大西洋白雪松森林的植物种类与池松林、波科辛林和混合常绿非河流沼泽森林相似。它们与两者都不同,因为林冠层占主导地位且灌木密度较低,并且与以前长期遭受灾难性火灾的大片泥炭地有关。泥炭地大西洋白雪松森林在全球范围内都很稀有,由于大规模砍伐和减少火灾,其分布范围现已减少到原来的小规模残余。由于这些干扰和大规模的开沟,大沼泽地的许多前林地已经变成了以红枫和沼泽树为主的非河流沼泽森林。大西洋白雪松是稀有蝴蝶黑纹蝶( Mitoura hesseli )的幼虫寄主,这种蝴蝶曾在大沼泽地被发现。
参考文献:Dabel 和 Day ( 1977 )、Day ( 1985 )、Dean ( 1969 )、Fleming 和 Moorhead ( 1998 )、Frost ( 1995 )、Stevens 和 Patterson ( 1998 )、Train 和 Day ( 1982 )。 © DCR-DNH, Caren Caljouw.
© DCR-DNH, Caren Caljouw.
 下载下面列出的每个社区类型的组成汇总统计电子表格。
下载下面列出的每个社区类型的组成汇总统计电子表格。