 自然保护与休闲部
自然保护与休闲部保护·守护·共享
 自然保护与休闲部
自然保护与休闲部 目录
目录里奇湾森林
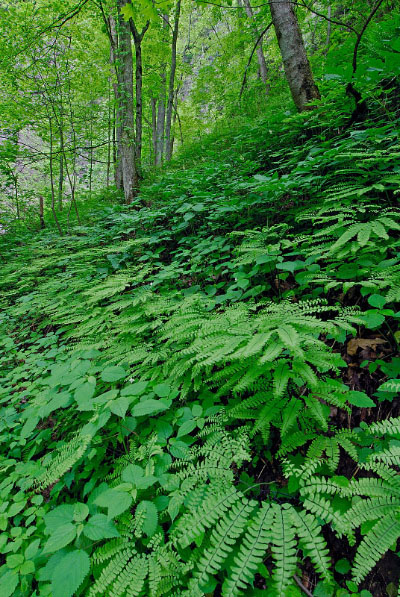
The mixed hardwood forests of this group occupy fertile, mesic, mountain-slope habitats at elevations ranging from about 300 m (1,000 ft) commonly to 1,100 m (3,600 ft), and occasionally higher. Distributed locally throughout western Virginia, these forests are strongly associated with moist, sheltered, landforms (i.e., coves, ravines, and concave lower slopes). Soils may be weathered from various substrates but are generally moderately acidic to moderately alkaline, with high base saturation. In these habitats, soil fertility appears to be strongly correlated with high base cation levels (particularly calcium, magnesium, and manganese) rather than with high pH, and higher-elevation sites often have soils with surprisingly low pH. Characteristic trees include sugar maple (Acer saccharum), basswoods (Tilia americana var. americana and var. heterophylla), white ash (Fraxinus americana), tulip-tree (Liriodendron tulipifera), bitternut hickory (Carya cordiformis) and yellow buckeye (Aesculus flava); chiefly south of the James River). Herbaceous growth is lush with spring ephemerals and leafy, shade-tolerant forbs such as blue cohosh (Caulophyllum thalictroides), yellow jewelweed (Impatiens pallida), large-flowered trillium (Trillium grandiflorum), wood-nettle (Laportea canadensis), common black cohosh (Actaea racemosa), sweet cicely (Osmorhiza claytonii), Virginia waterleaf (Hydrophyllum virginianum), large-leaf waterleaf (Hydrophyllum macrophyllum), large-flowered bellwort (Uvularia grandiflora), red trillium (Trillium erectum), yellow violets (Viola pubescens and Viola eriocarpa), white baneberry (Actaea pachypoda), two-leaved miterwort (Mitella diphylla), goat's-beard (Aruncus dioicus var. dioicus,), yellow mandarin (Prosartes lanuginosa), showy skullcap (Scutellaria serrata), eastern blue-eyed-mary (Collinsia verna), Guyandotte beauty (Synandra hispidula), glade fern (Homalosorus pycnocarpos), and many others. Compositional variation related to substrate and elevation is complex but the group partitions convincingly into several major community types. The principal threats to rich cove forests are logging and invasion by shade-tolerant, non-native weeds, especially garlic-mustard (Alliaria petiolata). The frequent to common white ash component of these communities is undergoing widespread mortality from Emerald Ash Borer outbreaks.
富饶的海湾森林和斜坡森林与类似的基本中生代森林的区别在于,前者分布范围更有限,多为山地分布;后者出现在较高的海拔地区;植物区系组成以阿巴拉契亚山脉和高海拔地区的主要物种为主。
参考文献:Coulling 和 Rawinski ( 1999 )、Fleming ( 1999 )、Fleming 和 Coulling ( 2001 )、Fleming 和 Moorhead ( 1996 )、Fleming 和 Moorhead ( 2000 )、Johnson 和 Ware ( 1982 )、Olson 和 Hupp ( 1986 )、Rawinski 等人 ( 1994 )、Rawinski 等人 ( 1996 )、Rheinhardt 和 Ware ( 1984 )。

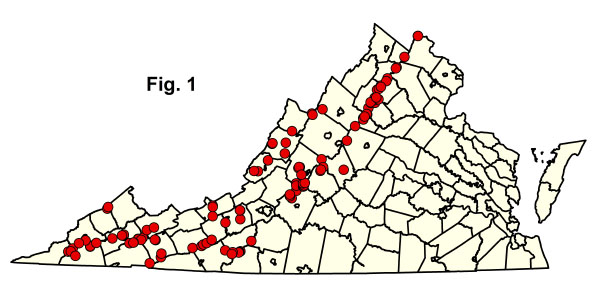
该组的分类基于对弗吉尼亚州34县采样的119地块的分析(图1 )。大多数地块也在国家公园管理局的各种跨州、区域分类工作中进行了分析(例如,国家首都地区和阿巴拉契亚山道植被测绘项目)。需要收集一些额外的数据来确定四种分类类型的完整州内地理范围。单击下面任何突出显示的 CEGL 代码即可查看NatureServe Explorer 提供的全球 USNVC 描述。
 下载下面列出的每个社区类型的组成汇总统计电子表格。
下载下面列出的每个社区类型的组成汇总统计电子表格。