 自然保护与休闲部
自然保护与休闲部保护·守护·共享
 自然保护与休闲部
自然保护与休闲部 目录
目录沿海平原/山麓橡树 - 山毛榉/荒地森林
In Virginia, forests of this group are widely but locally distributed in small to occasionally large patches across much of the dissected, inner Coastal Plain and Piedmont. Similar forests are known from North Carolina, South Carolina, and Maryland. Typical habitats are submesic, usually north-facing bluffs, and steep ravine slopes with acidic, nutrient-poor soils. Over most of the state, white oak (Quercus alba), northern red oak (Quercus rubra), chestnut oak (Quercus montana), and American beech (Fagus grandifolia) are the major overstory trees. In the southeastern Virginia Coastal Plain, southern red oak (Quercus falcata) and water oak (Quercus nigra) are prominent. Eastern hemlock (Tsuga canadensis) and sweet birch (Betula lenta var. lenta) are occasional associates in the Piedmont. Sourwood (Oxydendrum arboreum), blackgum (Nyssa sylvatica), red maple (Acer rubrum), American holly (Ilex opaca var. opaca) and, in southeastern Virginia, common sweetleaf (Symplocos tinctoria) are common understory trees. Dense colonies of mountain laurel (Kalmia latifolia) or, very locally, great rhododendron (Rhododendron maximum) form a continuous shrub layer. Few herbaceous species occur in the stands. On very steep and rocky bluffs, tree canopies may be quite open as the result of poor establishment and frequent downfalls. Communities in this group are similar to Mesic Mixed Hardwood Forests but usually occupy drier, steeper sites that support fewer mesophytic plants and a greater abundance of heaths.
参考文献:Fleming ( 2002 a)、Walton等人( 2001 )。
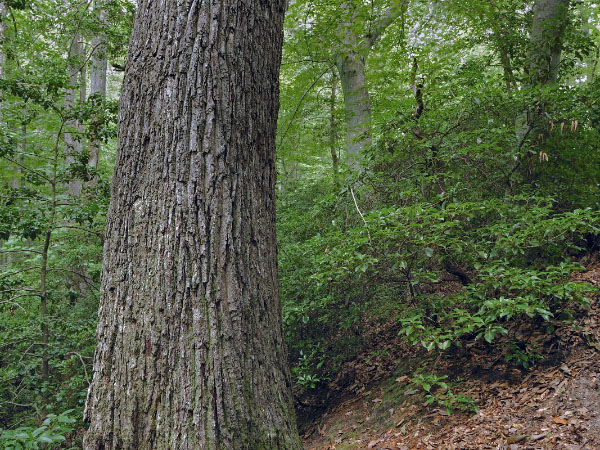 © DCR-DNH,加里·P·弗莱明。
© DCR-DNH,加里·P·弗莱明。
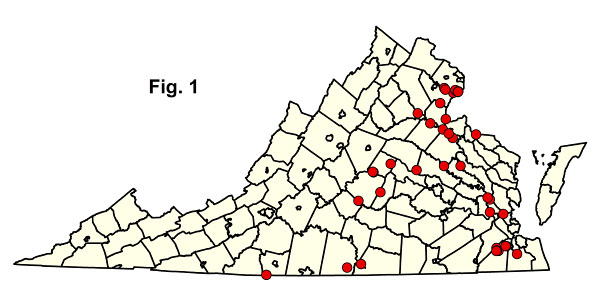
根据对39地块样本数据的区域分析,已将社区划分为两种地理上离散的社区类型(图1 )。单击下面任何突出显示的 CEGL 代码即可查看NatureServe Explorer 提供的全球 USNVC 描述。
 下载下面列出的每个社区类型的组成汇总统计电子表格。
下载下面列出的每个社区类型的组成汇总统计电子表格。